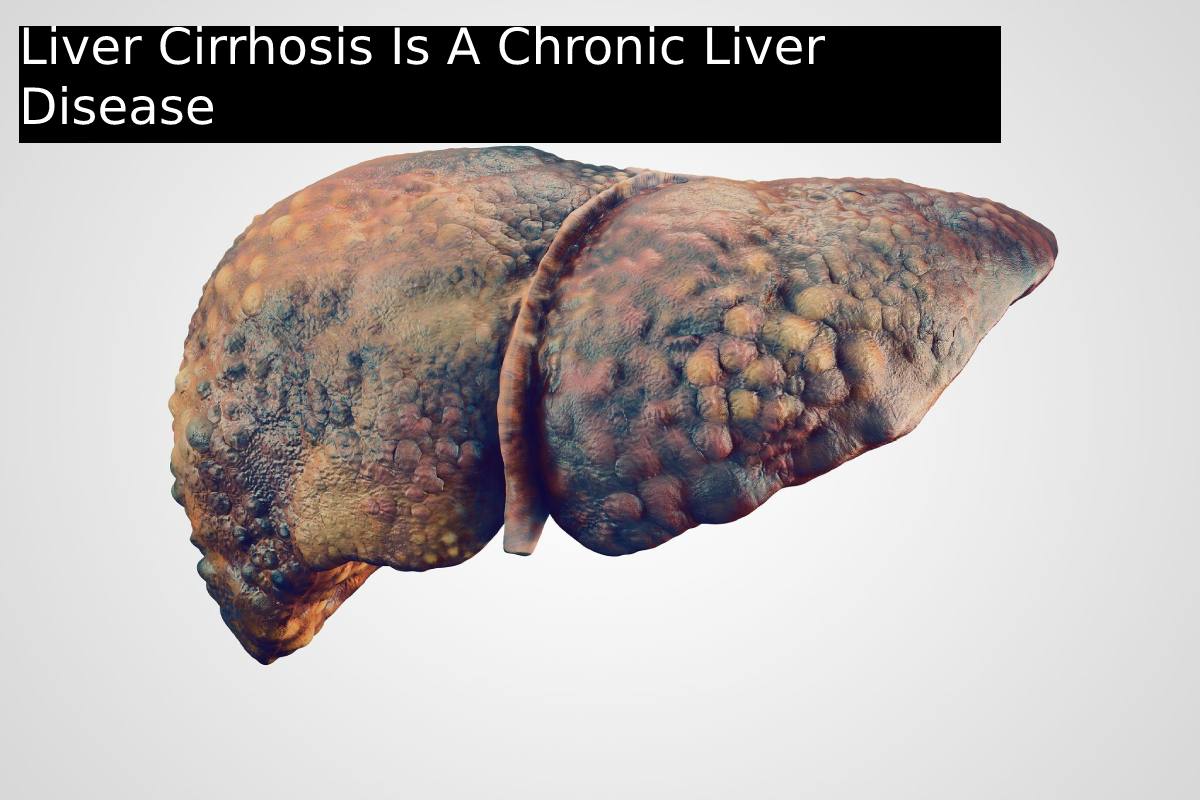
Liver Cirrhosis
INCREASED HARDNESS OF LIVER TISSUE
[Liver cirrhosis]is a chronic liver disease associated with progressive scarring of liver tissue (necrosis).
. The liver shrinks over time as healthy liver cells die and are swapped by scar tissue. The scar tissue progressively hardens. As a result, important metabolic and detoxification functions, which the organ assumes in the body, are impaired in liver cirrhosis.
In Germany, at least 3 million people suffer from liver diseases, of which between 0.7 and 1% suffer from liver cirrhosis.
Symptoms Of Liver Cirrhosis
CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER IS ACCOMPANIED BY SEVERAL SYMPTOMS
reduction
jaundice (jaundice)
loss of appetite
malnutrition
abundance
weightloss
gas
Spider-like vascular markings on the skin (spider nevi)
uncharacteristic discomfort in the upper abdomen
stomach ache
Redness of the palms (palm erythema)
Causes Of Liver Cirrhosis
ALCOHOL LEADS TO CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER IN ABOUT HALF OF CASES
When determining the most common causes of liver cirrhosis, those affected by a high regular consumption of alcohol constitute the largest proportion, around 50%. The truth is that men who regularly drink more than 60 g of pure alcohol per day for more than 10 years have an increased risk of developing liver cirrhosis. For women, on the other hand, a daily consumption of more than 20 g is considered risky.
However, according to Deutsches Ärzteblatt (2012; 109/17), many heavy drinkers do not develop liver cirrhosis. Based on the results of previous studies, experts assume that genetic causes are responsible for this result.
Viral Cirrhosis Of The Liver
In about 25% of cases, liver cirrhosis is the result of viral inflammation (viral hepatitis) that has not healed and has taken a chronic aggressive course. Various viruses that cause hepatitis are responsible for this.
Liver cirrhosis due to autoimmune hepatitis
Furthermore, wrinkled liver is also caused by autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune hepatitis, in which the body’s immune system attacks liver cells. Chronic inflammation of the bile ducts (primary biliary cirrhosis) with an unclear cause may also be the trigger.
Other Possible Causes
Chronic diseases of the bile ducts with biliary obstruction
Metabolic diseases such as Wilson’s disease (copper storage disease) or hemochromatosis (iron storage disease)
poisoning (carbon tetrachloride)
medicine
Diagnosis of [liver cirrhosis]
Several Investigations Require
In addition to the diagnosis, which can be confirmed by blood tests, ultrasound (ultrasound), and liver biopsy (removal of tissue), additional tests should clarify the causes and record complications. In [liver cirrhosis], there is a reduced amount of albumin (protein from the group of plasma proteins) and a reduced Quick value (test for the diagnosis of blood coagulation disorders) in the blood, while the ESR (reduced the rate of blood cells for the detection of inflammatory processes) and transaminases are elevated, which can be detected in tissues and blood when cell membranes are leaky.
course of [liver cirrhosis]
SERIOUS CONSEQUENCES ARE POSSIBLE
Tissue damage to the organ caused by [liver cirrhosis] is irreversible and, if left untreated, leads to liver failure, liver cancer, or kidney failure.
Common Complications
Circulatory disturbance in the liver increases pressure in the portal vein (portal hypertension) and bypass circulation (varicose veins) occurs.
Potential Impact of Complications
Increased liver dysfunction
Internal bleeding from varicose veins (esophageal varices)
Accumulation of water in the tissue, usually in the abdomen (ascites)
Expansion of abdominal cutaneous veins (Caput medusae)
Impaired brain function with confusion, incoordination, tremors, apathy, coma, drowsiness, typical fresh liver odor on the breath (portosystemic encephalopathy)
enlarged spleen
hormonal disorders
malnutrition
[liver cirrhosis]therapy
Possible Therapies
In addition to treating the underlying disease, [liver cirrhosis] patients are always advised to take care of their body and lead a normal life. There is an absolute ban on alcohol. Otherwise, the treatment depends on the individual case:
In case of vitamin deficiency, an adequate vitamin intake is made
Treatment of bleeding disorders with coagulation factors
Liver transplant in individual cases
Treatment for ascites: possibly ascites puncture